Carbon fiber is widely used in high-end engineering due to its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance. However, neglecting certain safety measures may reduce material performance, risk worker safety, and shorten product life. GBTECH offers the following key recommendations to ensure safe and effective carbon fiber use.
1. Avoid Strong Solvents and Oxidizers
Carbon fiber composites are usually based on epoxy or phenolic resins. Strong solvents like acetone, DMF, and THF can soften or swell the resin, reducing adhesion, fatigue resistance, and interface durability.
More hazardous are acids and oxidizers such as nitric acid, bleach (NaClO), and hot acetic acid. These can cause surface oxidation (producing CO, CO₂), microcracks, and loss of toughness and strength. Acid vapors may release corrosive gases (e.g., HCl), endangering both health and equipment.
GBTECH recommends: Never clean carbon fiber with strong solvents or concentrated acids. If chemical treatment is required, perform it in sealed, corrosion-resistant environments with chemical PPE, proper ventilation, and waste recycling systems.
Carbon fiber itself is thermally stable, but resin matrices degrade above 150–180°C, and interfaces fail around 300°C. Air oxidation of carbon fiber begins at >450°C, reducing structural integrity. NASA experiments show performance drops at 450–700K (180–430°C).
High humidity (>60% RH) weakens the fiber–resin interface, causing delamination and lower fatigue life. UV exposure accelerates surface yellowing and cracking. GBTECH recommends controlling temp ≤150°C, humidity ≤60%, and applying UV-resistant coatings when used outdoors.
Cutting or grinding carbon fiber generates fine dust. Use HEPA-filtered respirators and vacuum exhaust systems. Isolate workspaces and install local ventilation fans.
Wear long-sleeve protective clothing, gloves, and goggles to prevent skin injuries and chemical exposure. Since carbon fiber is electrically conductive, regularly clean dust near equipment to avoid short circuits or static sparks.
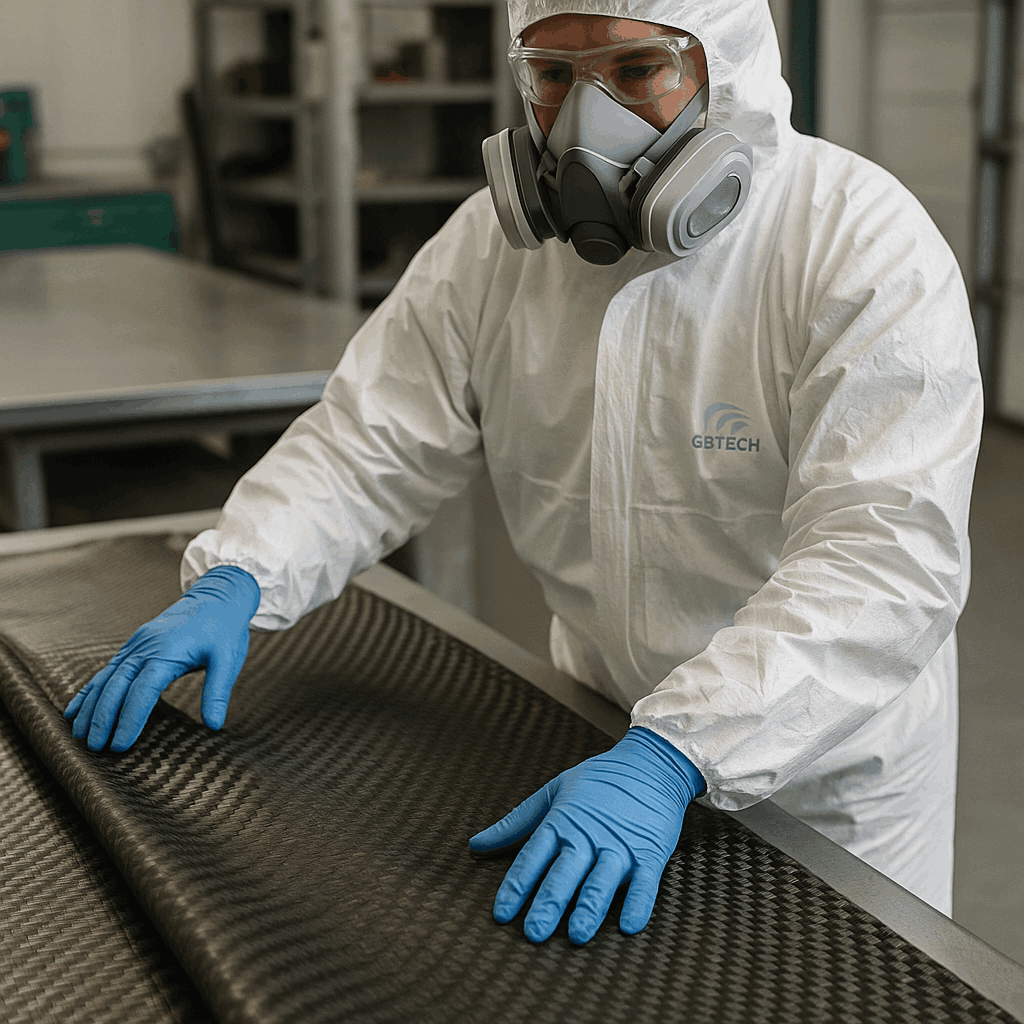

Carbon fiber is not easily flammable, but resins may ignite at high temperatures, releasing toxic gases (CO, HCN). Equip all work/storage areas with dry powder or CO₂ extinguishers. Keep materials away from heat/flames and ensure good ventilation or oxygen isolation during high-temp work.
Clean parts regularly using neutral detergent with a soft cloth, followed by dry wiping. Inspect for cracks or delamination and repair with resin or coatings when needed. Apply UV protection for outdoor use and recoat periodically.
Advanced methods like hot acetic acid + ZnCl₂ can separate resin from carbon fiber with >94% recovery. However, they require high-temperature, closed-loop systems with risk of corrosion and toxicity.
GBTECH advises setting up dedicated recovery zones, sealed reactors, and proper sorting. Burning or landfill disposal is strictly prohibited. Favor chemical or thermal recycling and secondary use of recovered fibers.
- Avoid direct contact with strong solvents or acids.
- Maintain working temperature ≤150°C, humidity ≤60%, and apply UV protection.
- Wear PPE and ensure effective ventilation during processing.
- Clean conductive dust regularly to prevent short circuits.
- Keep fire extinguishers ready and avoid ignition sources.
- Clean and inspect components regularly to preserve performance.
- Set up closed-loop recovery for waste management and recycling.
